What are Alzheimer's Plaques and Tangles?
Written By: Caleigh Findley, PhD
Reviewed By: Sharyn Rossi, PhD, Senior Director, Neuroscience Programs, BrightFocus Foundation
Written By: Caleigh Findley, PhD
Reviewed By: Sharyn Rossi, PhD, Senior Director, Neuroscience Programs, BrightFocus Foundation
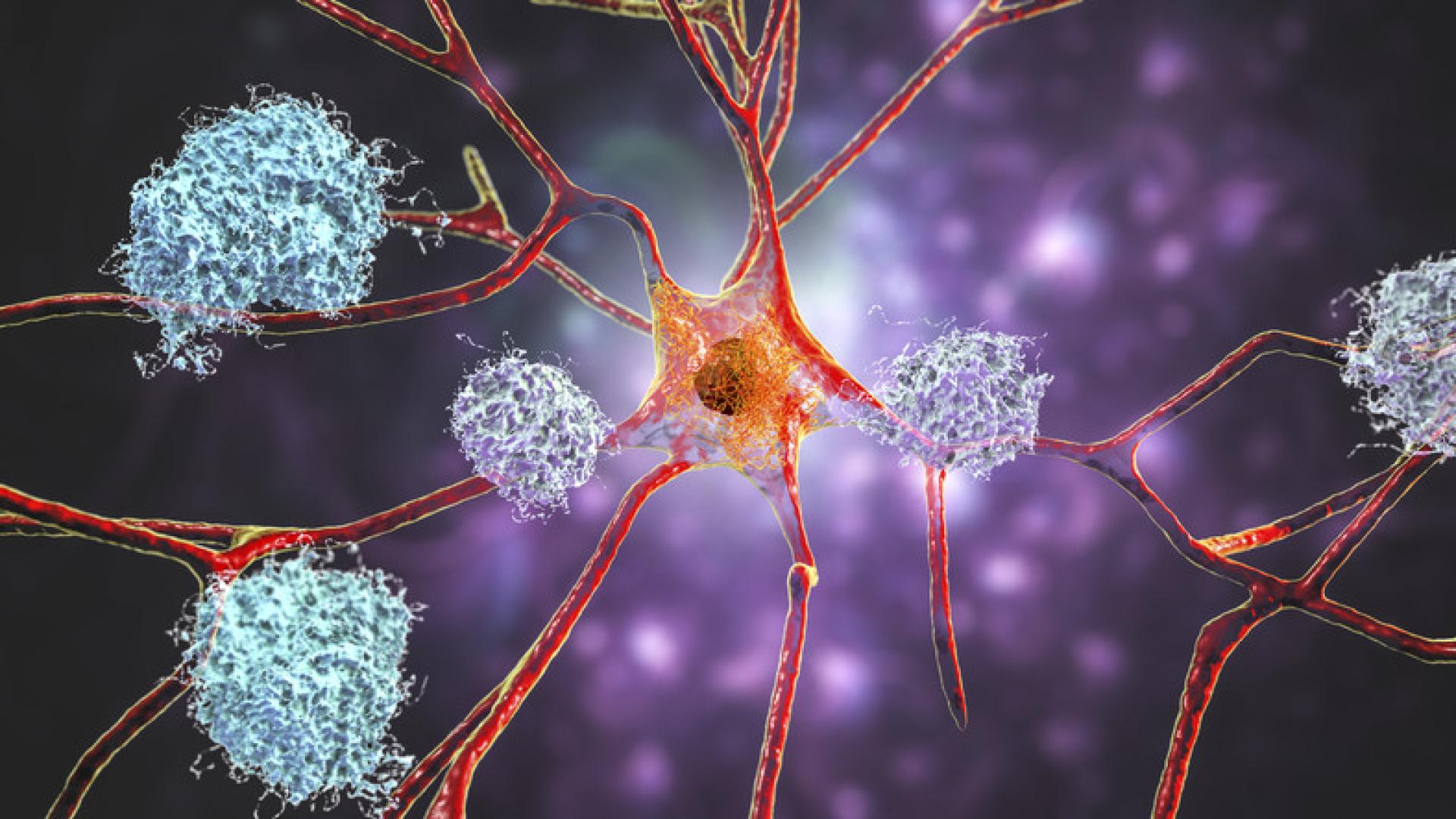
Alzheimer’s disease, the most common type of dementia, has two hallmark signs that appear in the brain: amyloid plaques and tau tangles. These misshapen proteins remain the most well-known and frequently studied indicators of Alzheimer’s.
Learn more about the role of amyloid-beta and tau in Alzheimer’s disease.
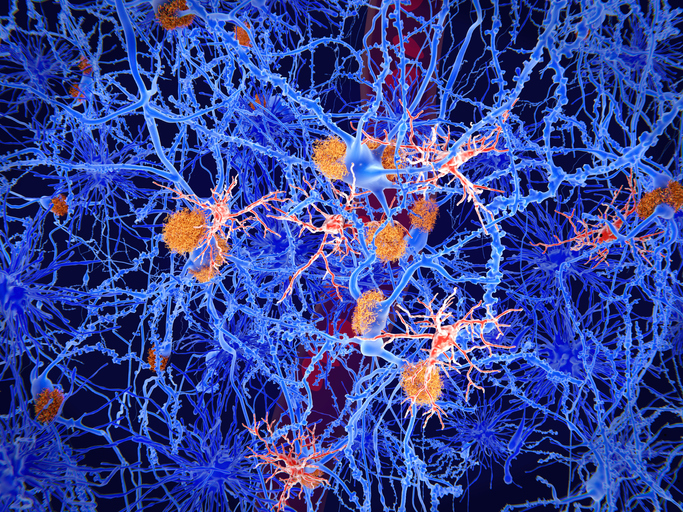
Amyloids are protein fragments produced from the amyloid precursor protein (APP) that can group together and form clumps in various organs and tissues, including the liver, kidneys, and brain. APP plays an important role in many of the basic functions of brain cells responsible for communication, called neurons. It helps neurons develop, talk to one another, and stay in harmony, among other supportive roles.
However, depending on the length of the amyloid protein produced, it can have harmful effects on the brain. Amyloid-beta 42 (Aβ42) is considered the more toxic form for the brain because of its length and tendency to form clumps.
The brain has several processes in place to remove excess amyloid and keep the environment balanced. Some evidence shows that this system does not work properly in Alzheimer’s disease, allowing amyloid to build up and create plaques.
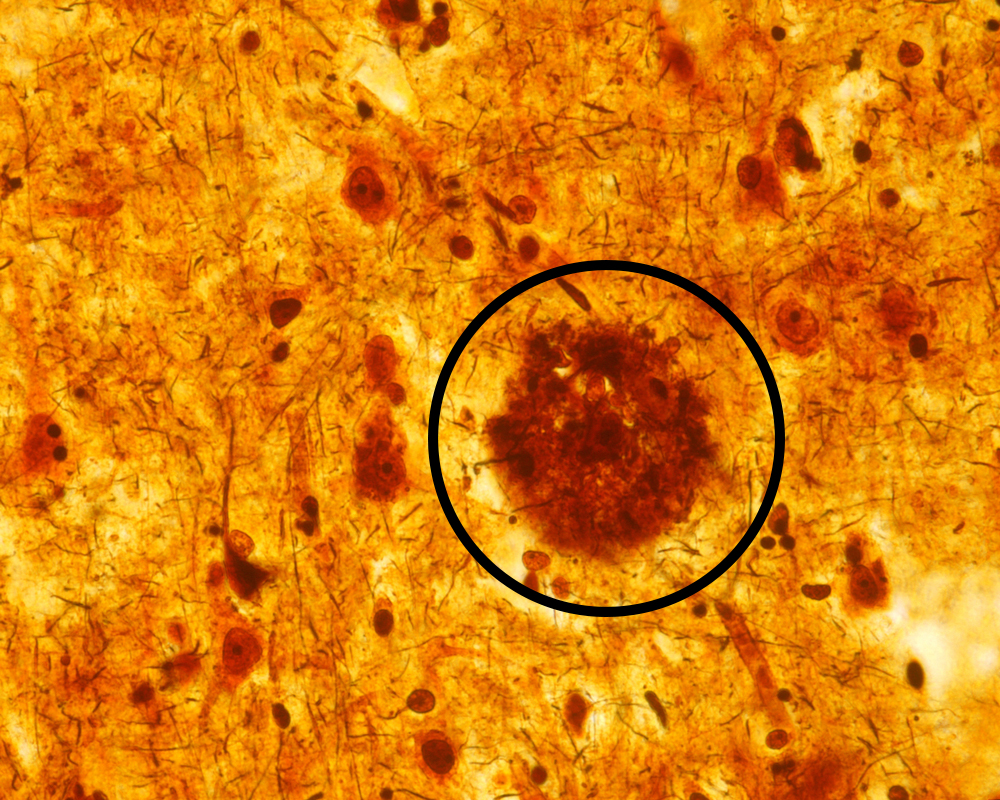
An overproduction of Aβ42 can occur for many reasons, including the presence of risk genes associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Other conditions may also drive up Aβ42 production, including a history of traumatic brain injury, circadian rhythm disturbance, and type 2 diabetes, among others.
When there is too much of this long sticky protein, it groups together into protein structures called oligomers. Amyloid oligomers are thought to be especially toxic, as they can interact with surrounding brain cells. The action of Aβ42 oligomers can impair cell function and contribute to Alzheimer’s disease progression.
With time, these oligomers come together in dense clumps, or plaques, that cannot be dissolved. Plaques exist in between brain cells, disrupting communication and causing inflammation and cell damage.
Clearing plaques from the brain has been a focus of drug development for many years. Scientists have engineered antibodies to target amyloid and help clear it from the brain—called “anti-amyloid” treatments.
This hypothesis empowered the first anti-amyloid therapy that received FDA expedited approval, called Aduhelm, targeting amyloid plaques. Unfortunately, clinical trials failed to show a clinically significant impact on Alzheimer’s symptoms, like memory loss.
Scientists are also targeting earlier versions of amyloid before they form plaques. The anti-amyloid therapy Leqembi works to clear plaques and this earlier form of amyloid. In a clinical trial of 1,800 participants, the drug slowed cognitive decline by an average of roughly 25% over 18 months.
Another highly anticipated anti-amyloid therapy, donanemab, will receive a final decision from the FDA in 2024. You can learn more about current (and upcoming) Alzheimer’s treatments here.
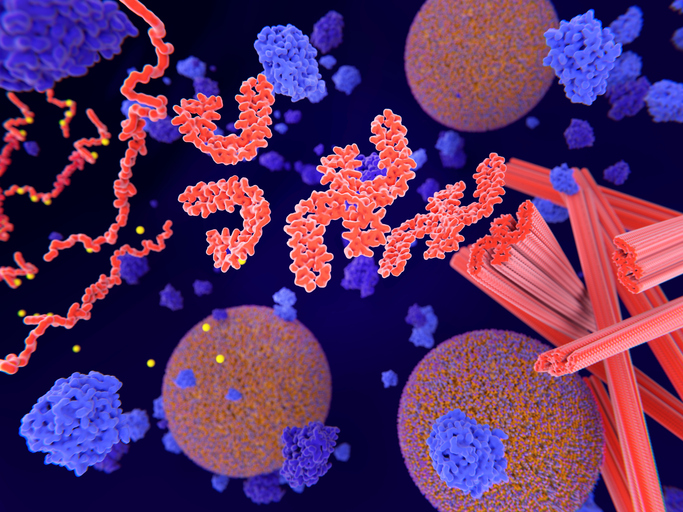
Tau is an important protein primarily found inside of neurons that supports the transport of nutrients and other molecules throughout the cell. This skeleton helps transport nutrients and other important substances from one part of the nerve cell to another.
To do its job, the tau protein must be folded in a certain way to connect with microtubules. When changes to tau’s structure or misfolding occur, as in Alzheimer’s disease, it can no longer perform this function. The abnormal tau begins to build up inside the cell, and the skeleton framework collapses.
Tau also has a smaller oligomer form that exists in the spaces between neurons. In high levels, tau oligomers may also interfere with surrounding brain cells. Elevated tau levels are observed in the brain decades before the onset of Alzheimer’s disease symptoms.
The accumulation of abnormal tau leads to sticky, thread-like structures called neurofibrillary tangles. This buildup prevents tau from doing its job, damaging the neuron’s inner skeleton and impairing communication between cells.
There are no FDA-approved therapies specifically targeting tau. However, several therapies have undergone clinical trials. These primarily act to stabilize microtubules, prevent tau abnormalities, and stop the buildup of tangles. Anti-tau antibodies are also underway but are in the early stages of clinical trial development and testing.
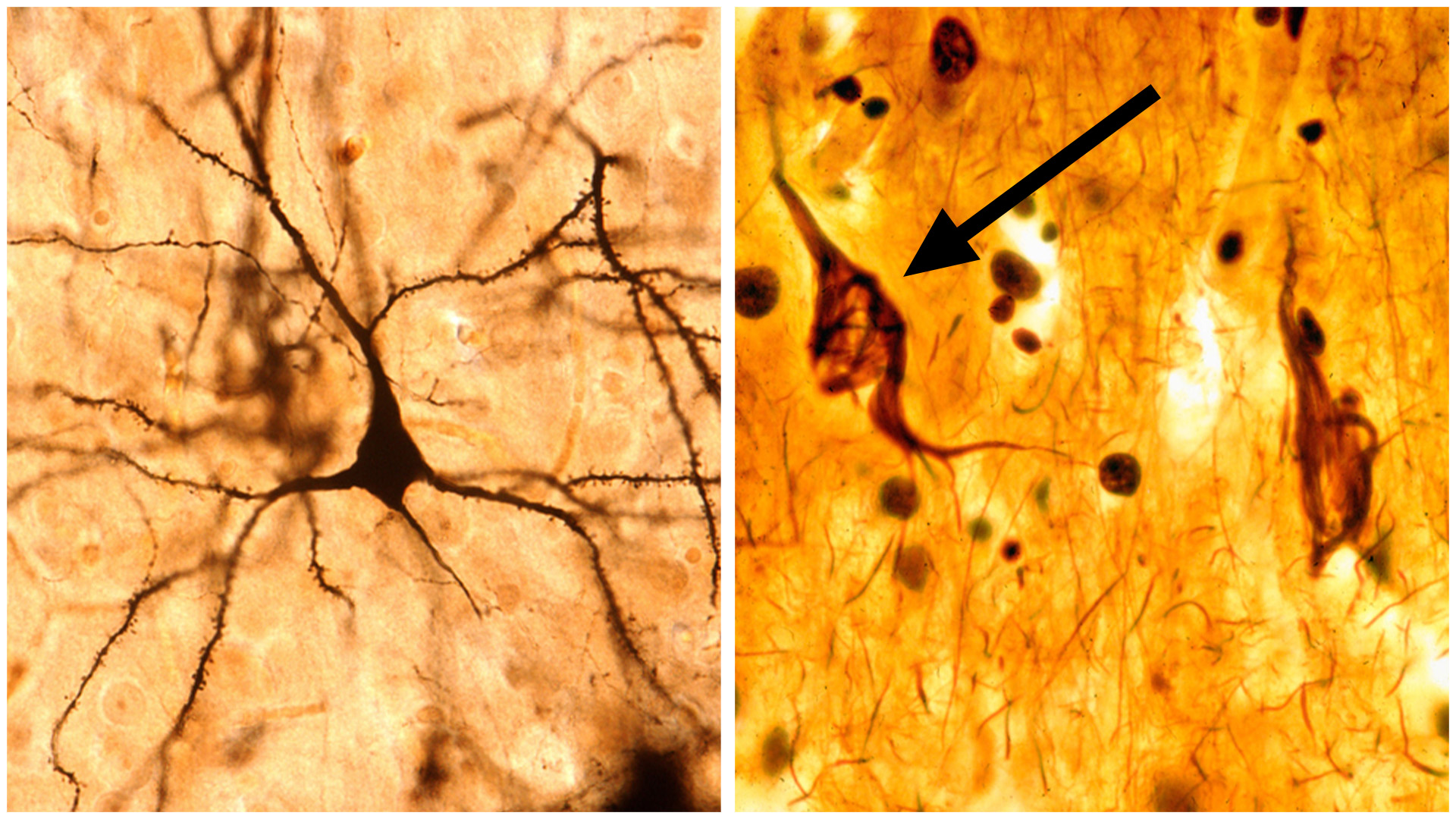
When neurons struggle to communicate with one another, it can have a wide-spanning impact depending on the brain area affected. The buildup of toxic proteins in brain regions associated with learning, memory, personality, and decision-making are directly linked to some of the initial symptoms that appear in Alzheimer’s disease, like impulsive decision making or trouble with short-term memory.
As the disease progresses, brain cells experience an overwhelming amount of energy imbalance, inflammation, and cell damage. The brain executes an emergency response plan when these plaques and tangles appear, including immune defense, cell repair, and various attempts to restore balance to the environment. These mechanisms are eventually overcome by the disease, resulting in cell death and brain volume loss.
It remains unclear if amyloid plaques and tau tangles can be prevented. However, studies have shown that a proper diet and regular exercise can decrease Alzheimer’s risk and potentially slow disease progression. Learn more about how to protect your brain health here.
BrightFocus Foundation is a premier global nonprofit funder of research to defeat Alzheimer’s, macular degeneration, and glaucoma. Since its inception more than 50 years ago, BrightFocus and its flagship research programs—Alzheimer’s Disease Research, Macular Degeneration Research, and National Glaucoma Research—has awarded more than $300 million in research grants to scientists around the world, catalyzing thousands of scientific breakthroughs, life-enhancing treatments, and diagnostic tools. We also share the latest research findings, expert information, and resources to empower the millions impacted by these devastating diseases. Learn more at brightfocus.org.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is a public service of BrightFocus Foundation and is not intended to constitute medical advice. Please consult your physician for personalized medical, dietary, and/or exercise advice. Any medications or supplements should only be taken under medical supervision. BrightFocus Foundation does not endorse any medical products or therapies.
Every Donation is a Step Forward in the Fight Against Alzheimer’s
Your donation powers cutting-edge research and helps scientists explore new treatments. Help bring us closer to a cure and provide valuable information to the public.
Donate Today